Running Python Scripts From C++ ( and Umfeld )
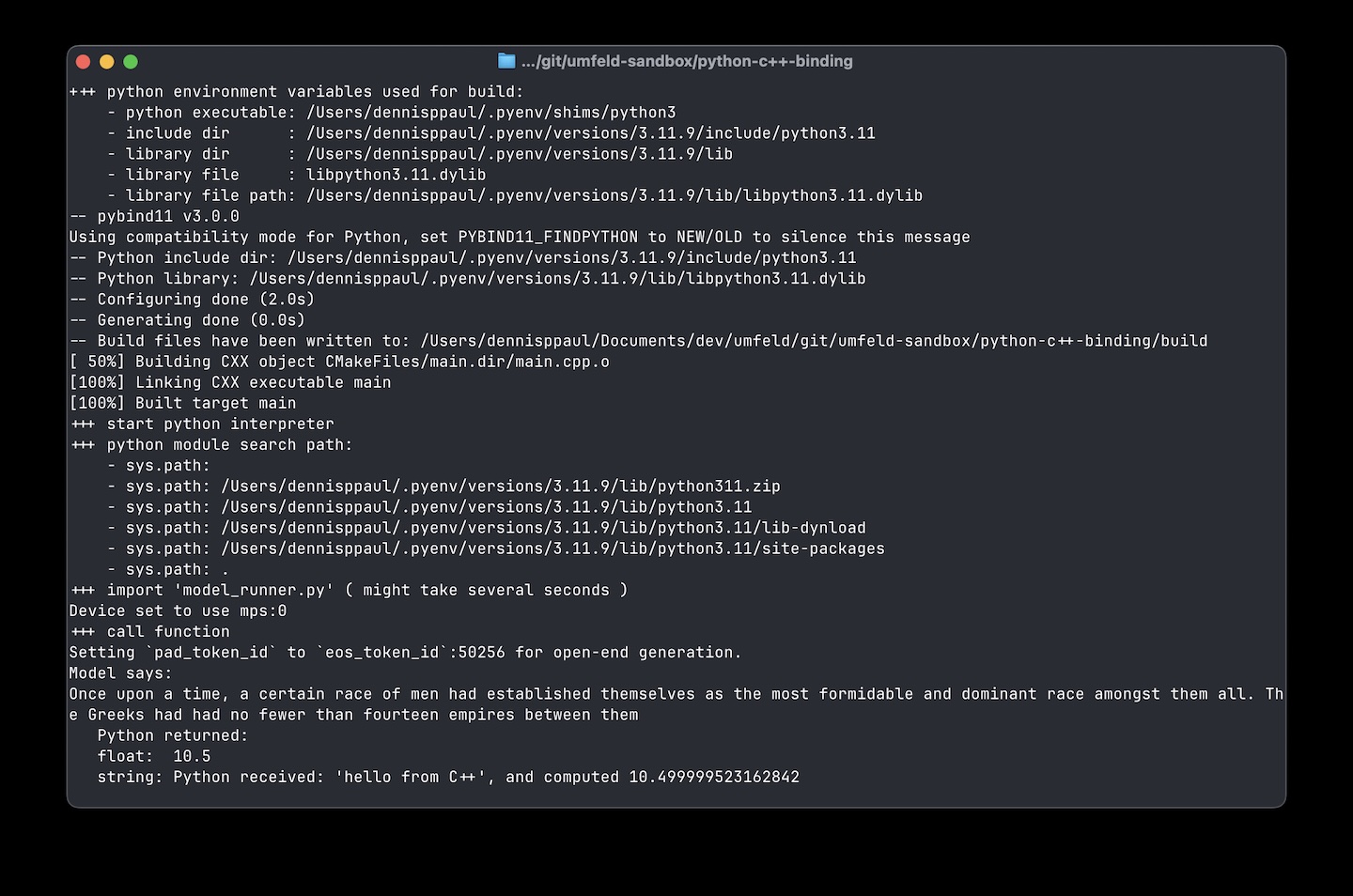
on a tiny-little weekend project i looked into running python scripts from C++. it was surprisingly simple! i used pybind11 and tested interfacing with a Hugging Face transformer to communicate with GPT2 and also passed and returned float and std::string from C++ to python and back.
i wrapped in a CMake script. this is what i ended up with … just a proof of concept:
CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_policy(SET CMP0148 OLD)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)
project(HF_Embed)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
# test with pybind11 v2.13.6 (2024-09-14)
include(FetchContent)
FetchContent_Declare(
pybind11
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/pybind/pybind11.git
GIT_TAG master
)
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(pybind11)
find_package(Python3 REQUIRED COMPONENTS Interpreter Development)
message(STATUS "Python include dir: ${Python3_INCLUDE_DIRS}")
message(STATUS "Python library: ${Python3_LIBRARIES}")
add_executable(main main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main PRIVATE pybind11::embed Python3::Python)
model_runner.py:
from transformers import pipeline
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model="gpt2")
def run_model(prompt):
output = generator(prompt, max_new_tokens=30)
return output[0]["generated_text"]
def process_data(number: float, message: str) -> tuple[float, str]:
result = number * 2.5
new_message = f"Python received: '{message}', and computed {result}"
return result, new_message
main.cpp:
#include <pybind11/embed.h>
#include <iostream>
namespace py = pybind11;
int main() {
std::cout << "+++ start python interpreter" << std::endl;
py::scoped_interpreter guard{}; // Start Python
try {
// Optionally add current directory to sys.path
py::module_ sys = py::module_::import("sys");
sys.attr("path").attr("append")(".");
std::cout << "+++ python module search path:" << std::endl;
py::list paths = sys.attr("path");
for (auto path : paths) {
std::cout << " - sys.path: " << std::string(py::str(path)) << std::endl;
}
// import model_runner.py
std::cout << "+++ import 'model_runner.py' ( might take several seconds )" << std::endl;
py::module_ model_runner = py::module_::import("model_runner");
// call LLM function
std::cout << "+++ call function" << std::endl;
py::object result_llm = model_runner.attr("run_model")("Once upon a time,");
std::cout << "Model says:\n" << result_llm.cast<std::string>() << std::endl;
// exchange data between C++ and python
float input_number = 4.2f;
std::string input_message = "hello from C++";
py::object result = model_runner.attr("process_data")(input_number, input_message);
// unpack the tuple result
auto tuple_result = result.cast<std::tuple<float, std::string>>();
float returned_float = std::get<0>(tuple_result);
std::string returned_string = std::get<1>(tuple_result);
// print results
std::cout << " Python returned:\n"
<< " float: " << returned_float << "\n"
<< " string: " << returned_string << std::endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "Python error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
and this is shell script to build and run the test. the script is a bit much ( e.g generating CMakePresets.json to configure local python environment ) but i tried to find a way to make it generic enough to maybe incorporate it into Umfeld at some point:
#! /bin/zsh
# set python env variables
# initialize pyenv if not already loaded
if command -v pyenv > /dev/null; then
export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"
export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PATH"
eval "$(pyenv init --path)"
eval "$(pyenv init -)"
fi
export PYENV_ROOT=$(pyenv root)
export PYTHON_ROOT=$(pyenv prefix)
PYTHON_EXEC=$(which python3)
PYTHON_PREFIX=$($PYTHON_EXEC -c 'import sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var("prefix"))')
PYTHON_INCLUDE=$($PYTHON_EXEC -c 'import sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_path("include"))')
PYTHON_LIBDIR=$($PYTHON_EXEC -c 'import sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var("LIBDIR"))')
PYTHON_LIBFILE=$($PYTHON_EXEC -c 'import sysconfig; print(sysconfig.get_config_var("LDLIBRARY"))')
PYTHON_LIBRARY="$PYTHON_LIBDIR/$PYTHON_LIBFILE"
echo "+++ python environment variables used for build: "
echo " - python executable: $PYTHON_EXEC"
echo " - include dir : $PYTHON_INCLUDE"
echo " - library dir : $PYTHON_LIBDIR"
echo " - library file : $PYTHON_LIBFILE"
echo " - library file path: $PYTHON_LIBRARY"
cat > CMakePresets.json <<EOF
{
"version": 3,
"configurePresets": [
{
"name": "system-python",
"generator": "Unix Makefiles",
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE": "Debug",
"Python3_EXECUTABLE": "${PYTHON_EXEC}",
"Python3_INCLUDE_DIR": "${PYTHON_INCLUDE}",
"Python3_LIBRARY": "${PYTHON_LIBRARY}",
"Python3_ROOT_DIR": "${PYTHON_PREFIX}"
}
}
]
}
EOF
# install transformer torch … only necessary once
pip -q install transformers torch
cmake -B build --preset system-python -Wno-dev
cmake --build build
./build/main